
In this tutorial, I have described how to calculate the mean, SD and SE by using Microsoft Excel. Then press the ‘enter’ button to calculate the SE. It is worth noting that instead of using the COUNT function, you can simply type in the number of values in the data set.

Enter the following into the cell: =STDEV( number1: number2)/SQRT(COUNT( number1: number2)) Click on an empty cell where you want the SE to be.Ģ. How To Calculate Standard Error in Excel (With. To calculate the SE in Excel, follow the steps below.ġ. Finally, calculate the weighted standard deviation by using Excel functions to create the formula from. The formula for the SE is the SD divided by the square root of the number of values n the data set (n). The standard error (SE), or standard error of the mean (SEM), is a value that corresponds to the standard deviation of a sampling distribution, relative to the mean value. How to calculate the standard error in Excel The way to solve it is to rewrite the weighted standard deviation formula. Then press the ‘enter’ button to calculate the SD. Then, as with the mean calculation, change the following:ģ. Enter the following formula =STDEV( number1: number2) To calculate the SD in Excel, follow the steps below.ġ Click on an empty cell where you want the SD to be.Ģ. The standard deviation (SD) is a value to indicate the spread of values around the mean value. How to calculate the standard deviation in Excel Then press the ‘enter’ button to calculate the mean value. You can simply click and drag on the values within Excel instead of typing the cell names.ģ.

There is no formula within Excel to use for this, so I will show you how to calculate this manually. These have built-in functions already available.Ĭalculating the standard error in Excel, however, is a bit trickier. The notation for standard error can be any one of SE, SEM (for standard error of measurement or mean), or S E.In this guide, I will show you how to calculate the mean (average), standard deviation (SD) and standard error of the mean (SEM) by using Microsoft Excel.Ĭalculating the mean and standard deviation in Excel is pretty easy. This weighted variance is given by 2 2 1 1 2 11 1 1 1 n ii w. SPSS approach SPSS uses a weighted variance as its estimate of 2. In other words, it is the actual or estimated standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the sample statistic. It is s2 given above that is used in WinCross, in conjunction with the effective sample size b, as the basis for the standard errors used in significance testing involving the weighted mean.
ERROR WEIGHTED STANDARD DEVIATION MANUAL
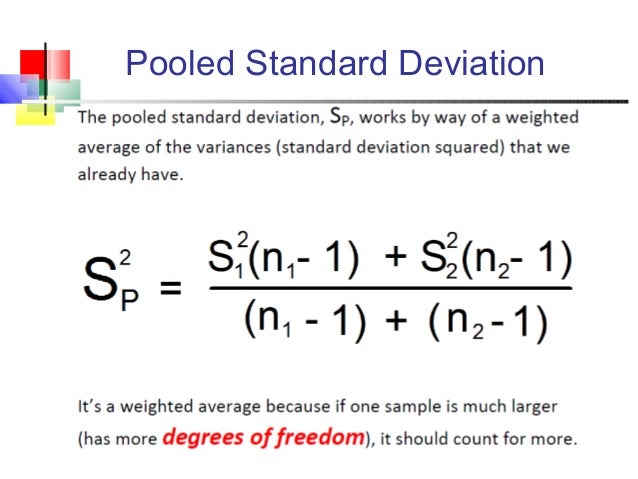
In particular, the standard error of a sample statistic (such as sample mean) is the actual or estimated standard deviation of the sample mean in the process by which it was generated. Statistics LET Subcommands WEIGHTED STANDARD DEVIATION DATAPLOT Reference Manual Septem2-67 PROGRAM LET Y DATA 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19 23 LET W DATA 1 1 0 0 4 1 2 1 0 LET A STANDARD DEVIATION Y LET AW WEIGHTED STANDARD DEVIATION Y W PRINT A AW The values of A and AW are 7.46 and 5.82 respectively. If a statistically independent sample of n In regression analysis, the term "standard error" refers either to the square root of the reduced chi-squared statistic, or the standard error for a particular regression coefficient (as used in, say, confidence intervals). In other words, the standard error of the mean is a measure of the dispersion of sample means around the population mean. Therefore, the relationship between the standard error of the mean and the standard deviation is such that, for a given sample size, the standard error of the mean equals the standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample size. This is because as the sample size increases, sample means cluster more closely around the population mean. With equal samples size, which is what you have, the standard deviation you are looking for is: Sqrt (.64 +. Mathematically, the variance of the sampling distribution obtained is equal to the variance of the population divided by the sample size. Why don't you just use the square root of the pooled (or weighted) variances. This forms a distribution of different means, and this distribution has its own mean and variance. The sampling distribution of a mean is generated by repeated sampling from the same population and recording of the sample means obtained. If the statistic is the sample mean, it is called the standard error of the mean ( SEM). The standard error ( SE) of a statistic (usually an estimate of a parameter) is the standard deviation of its sampling distribution or an estimate of that standard deviation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
